
- #WESTERN EUROPE FEUDAL KINGDOMS MAP FULL#
- #WESTERN EUROPE FEUDAL KINGDOMS MAP SERIES#
- #WESTERN EUROPE FEUDAL KINGDOMS MAP FREE#
Crusades opened up trade between Europe and cities of Constantinople and Alexandria.As a result a larger number of serfs self attained freedom. Some of the feudal lords who returned alive from the Crusades were forced to sell charter of liberties to towns which they once controlled.
#WESTERN EUROPE FEUDAL KINGDOMS MAP SERIES#
#WESTERN EUROPE FEUDAL KINGDOMS MAP FREE#
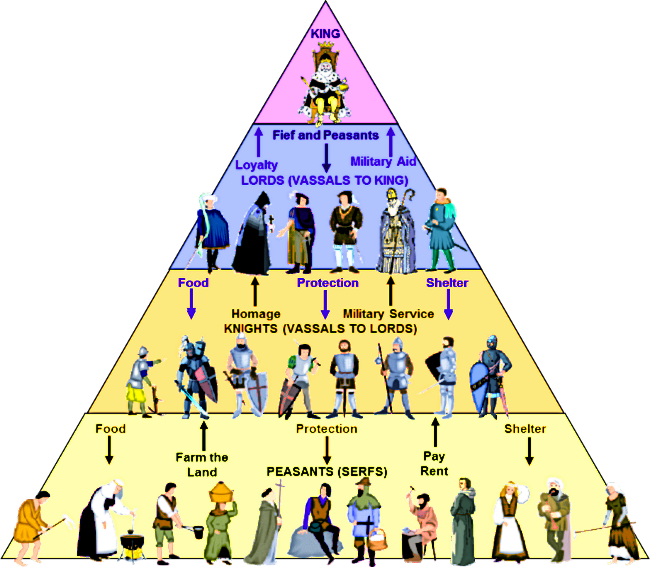
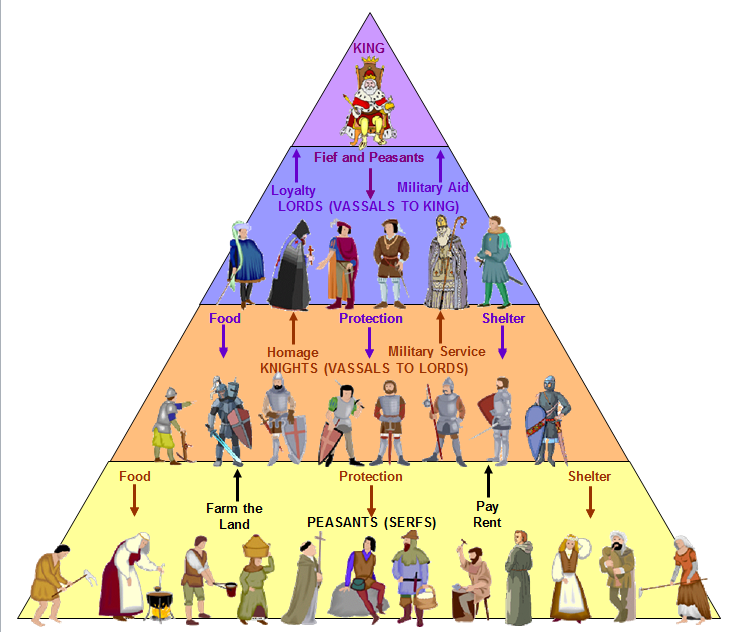
The serfs got an opportunity to free themselves of the feudal lords by taking up work in the new towns. With the growth of trade and commerce a number of new cities and towns grew which provided new opportunities for work. The liberation of the serfs due to enormous growth in trade and commence also greatly contributed to. The discovery of gun-powder and weapons like cannons also greatly helped the kings to reduce the lords to subjection and reduced their dependence on them. With the help of these armies they were able to bring the turbulent nobles under control. The middle classes consisting of traders and businessmen provided the king with money with which they began to maintain independent armies.
#WESTERN EUROPE FEUDAL KINGDOMS MAP FULL#
In this task they received full support from the newly emerged middle classes and freemen who were not under the control of the lords. In course of time when the feudal lords began to assert themselves too much, the kings who headed the feudal hierarchy, thought of bringing them under control. As Henry Martin has observed, “Feudalism concealed in its bosom the weapons with which it would be itself one day smitten”. The underlying reasons for this included warfare, disease, political change etc.įeudalism contained in itself the seeds of its destruction. But in the 14th century, Feudalism waned. Despite the social inequality it produced, Feudalism helped stabilize European society. The nobles who controlled these manors oversaw agricultural production and swore loyalty to the king. Under Feudalism, a monarch’s kingdom was divided and subdivided into agricultural estates called manors.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
